Is your label compliant with Packaging and Labelling Regulations?
Consumers around the world are becoming more conscious about their health and changing their lifestyles. From eating healthy food, exercising daily, and choosing healthy products while purchasing is becoming a part of their active lifestyle. One of the key factors which play an important role in choosing any healthy product is LABEL. An essential step to determine the purchase.
A label serves the following three primary functions, namely, basic product information, health, safety, and nutrition information and it also acts as a vehicle for food marketing, promotion, and advertising. It enlists important information’s like ingredients, additives, date of manufacturing, and other details so that the consumer can make an informed choice.
In a bid to encourage consumers to make healthier food choices, the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) have come up with a regulation for labelling products called Food Safety and Standards (Packaging and Labelling) Regulations, 2011. The FSSAI has been established under the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006, and it is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the regulation and supervision of food safety.
The Food Safety and Standards (Packaging & Labelling) Regulations, 2011 is divided into 2 chapters. Chapter 1 is for general guidelines and chapter 2 for packaging and labelling. Section 2.2.2. Labelling of pre-packaged food has a comprehensive set of guidelines that all the food product manufacturers and marketers should follow. In addition to the General Labelling requirements specified in 2.2.1, every package of food shall carry the following information on the label.
The Food Safety and Standards (Packaging & Labelling) Regulations, 2011 is divided into 2 chapters. Chapter 1 is for general guidelines and chapter 2 for packaging and labelling. Section 2.2.2. Labelling of pre-packaged food, has a comprehensive set of guidelines that all the food product manufacturers and marketers should follow. In addition to the General Labelling requirements specified in 2.2.1 every package of food shall carry the following information on the label.
- Name of the Food: The label of a pre-packaged food should have the name of the product, it can be a generic name- describing the food inside, trade name or brand name. It should be written in a clear font with appropriate font size as per the size of the pack.
- List of Ingredients: The list of ingredients should have all the ingredients used in the making of the product. It should be in descending order of their composition by weight or volume.
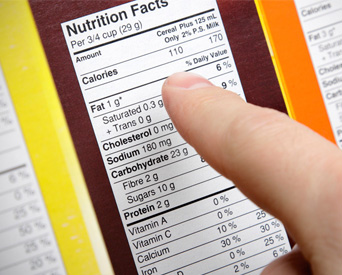
- Nutritional Information: Nutritional facts or nutritional information should be per 100gm/100ml/per serving of the product. It should contain:
- Energy value (Kcal)
- Amount of protein, carbohydrates (quantity of sugar) and fat in grams.
- Amount of any other nutrient for which a nutrition or health claim is made.
- Numerical information on vitamins & minerals, wherever declared, it shall be expressed in metric units.
- Where the nutrition declaration is made per serving, the amount in gram (g) or milliliter (ml) shall be included for reference beside the serving measure.
- Declaration regarding Vegetarian and Non-vegetarian food: Every package of vegetarian food shall bear a declaration to this effect made by a symbol and a colour code ‘green’ to indicate that the product, as well as ingredients used in the product, is vegetarian. Likewise, in case of non-vegetarian food, the symbol should consist of brown colour. The symbol should be in close proximity to the name or brand name on the package having a contrasting background on the principal display panel.
- Declaration regarding Food Additives: In addition to the ingredients in the product, additives should also be declared on the label. Food Additives falling in respective classes and appearing in lists of food additives permitted for use in foods generally, class titles shall be used with specific names or recognized international numerical identification.
- Name and Complete Address of the Manufacturer: Every package shall declare the name and complete address of the manufacturer and manufacturing unit. In case of imported food products, the package of food shall carry the name and complete address of the importer in India.
- Net Quantity: The net quantity of the product by weight/volume/number shall be declared on every product label.
- Batch No. /Lot. No. /Code No. : An identification mark in the form of the batch number, or code/lot number shall be given on the product label to trace in the manufacture or in distribution.
- Date of Manufacture or Packing: Every label of the food should have the date, month, and year in which the product is manufactured, packed, or pre-packed.
- Best Before and Use By Date: In order to avoid the consumption of the expired product, a best before date or use by date is given on the product, the month and year in capital letters up to which the product is best for consumption.
- Country of origin for Imported food: When the product is imported into India, the country of origin of the food shall be declared on the label.
- Instruction for Use: The instruction on how to use the product shall be given on the label, when the product requires reconstitution, for correct usage of the product.
The above information is mandatory for every pre-packaged food. As per the category and the ingredients used in the food product, the labelling will be more detailed. To comply with all the mandatory guidelines on the packaging and labelling Regulations, our experts at IRC will help you to ensure that the product labels are fully compliant with Indian Regulations.